Weekly Tech+Bio Highlights #13
In Brief; Spotlight; R&D Corner; Quick Hits; Companies to Watch (Precision Medicine +AI); Takeaway of the Week; Bonus Takeaway
Hi! I am Andrii Buvailo, and this is my weekly newsletter, ‘Where Tech Meets Bio,’ where I talk about technologies, breakthroughs, and great companies moving the biopharma and medtech industries forward.
If you've received it, then you either subscribed or someone forwarded it to you. If the latter is the case, subscribe by pressing this button:
Now, let’s get to this week’s topics!
In Brief
🔬 Researchers at Peking University introduced "ThermoFace," a non-invasive diagnostic tool that uses thermal facial imaging to assess biological age and predict metabolic diseases like diabetes and hypertension, showing promise as a rapid, cost-effective method for early disease detection and monitoring.
🔬 Blackrock Neurotech, backed by Tether, has enabled an ALS patient to regain speech using a brain-computer interface (BCI) that translates thoughts into spoken words at 62 words per minute, marking a significant milestone in neurological technology.
🔬 A Kaggle contest by Leash Bio reveals AI models struggle with predicting protein binding for novel molecules, highlighting their limitations in generalization. Leash Bio CEO Ian Quigley suggests that vastly larger datasets are needed to improve AI predictions, similar to advances in chess and protein folding.
🤝 Absci Corporation partners with Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center to develop up to six novel cancer therapeutics, combining Absci's generative AI platform with MSK's cancer research expertise, aiming for preclinical targets by the end of 2024.
💰 PLAIO, an Icelandic tech firm, raised €4.3 million to expand its AI-driven sales and operations planning platform for the pharmaceutical industry. The funds will be used to enhance its AI Coplanner tool and support global expansion, addressing inefficiencies in pharma supply chains by replacing outdated manual processes.
🧬 McGill researchers have developed a technique to manipulate stem cells by mechanically altering their nuclei, enabling precise differentiation into targeted cells like bone or fat. This breakthrough could pave the way for new stem cell therapies, with initial applications likely in bone regeneration. However, clinical treatments based on this discovery may take a decade or more to develop.
📈 23andMe shifts focus from drug discovery to the booming GLP-1 market, launching a telehealth weight loss program that prescribes these medications, while also initiating a large-scale genetic study to personalize treatment based on genetic responses.
🚀 Medable, Inc launches Medable Studio, a no-code electronic Clinical Outcome Assessment (eCOA) platform designed to streamline the configuration, translation, and deployment of clinical trials, reportedly reducing setup times from months to hours and offering increased transparency and control.
🌍 Basecamp Research and the country of Cameroon launch a pioneering access and benefit-sharing partnership, marking Cameroon as the first Central African country to implement such a deal for digital sequence information ahead of COP 16, the global biodiversity summit.
💡 Veridix AI, a subsidiary of the Emmes Group, has introduced protocol digitization within its Advantage eClinical Cloud, using AI and NLP to automate clinical trial study builds, reducing setup time by up to 30% and improving data accuracy.
🤝 OpenFold Consortium expands with six new members — Biogen, Congruence Therapeutics, POLARISqb, Psivant Therapeutics, SandboxAQ and Astex Pharmaceuticals — boosting its open-source AI tools for drug discovery, enhancing collaboration across biotech and pharma sectors to accelerate therapeutic innovation.
🤝 Persist AI and Nivagen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. are collaborating to develop an AI-driven manufacturing process for long-acting injectable drugs, aiming to simplify and accelerate the production and approval of these treatments, which improve patient adherence by providing sustained drug release.
💰 Halda Therapeutics secured $126 million in a Series B extension, bringing total funding to $202 million to advance its RIPTAC cancer therapies. The funds will support the development of Halda's lead candidate, HLD-0915, targeting metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, expected to enter Phase 1 trials in 2025.
🎯 Pfizer appoints Berta Rodriguez-Hervas as Chief AI and Analytics Officer, leveraging her expertise from Stellantis as a VP of Algorithms and ML Ops and NVIDIA to drive advancements in AI, machine learning, and analytics. She'll co-chair Pfizer's AI Council, focusing on accelerating drug discovery.
🔬 Indica Labs launches 11 new HALO AI Apps for tissue-based research, offering pre-trained classifiers and phenotypers that enhance image analysis across various cancer types—including breast, colorectal, gastric, ovarian, and NSCLC—aiming to accelerate research by reducing the need for custom model training.
🧠 Recursion announced the creation of "Neuromap", the world's first neuroscience phenomap, developed in collaboration with Roche and Genentech, triggering a $30 million milestone payment. Neuromap was created using over 1 trillion hiPSC-derived neuronal cells, advanced AI, and genetic perturbation techniques, aiming to accelerate neuroscience research and drug discovery.
Spotlight
🔬 Neuralink has successfully implanted its brain-computer interface in a second patient, allowing those with spinal cord injuries to control digital devices through thought alone. Elon Musk expects eight more patients to receive implants this year as part of ongoing clinical trials.
Watch my interview with Dr. Brian Jamieson, CTO of Diagnostic Biochips, were we talk about the opportunities and challenges of brain computer interfaces (BCI) technology, Neuralink, and the transformative potential of BCIs in neuroscience and pharmaceutical research: Ex-NASA Expert Unveils Everything You Need to Know About Brain-Computer Interfaces
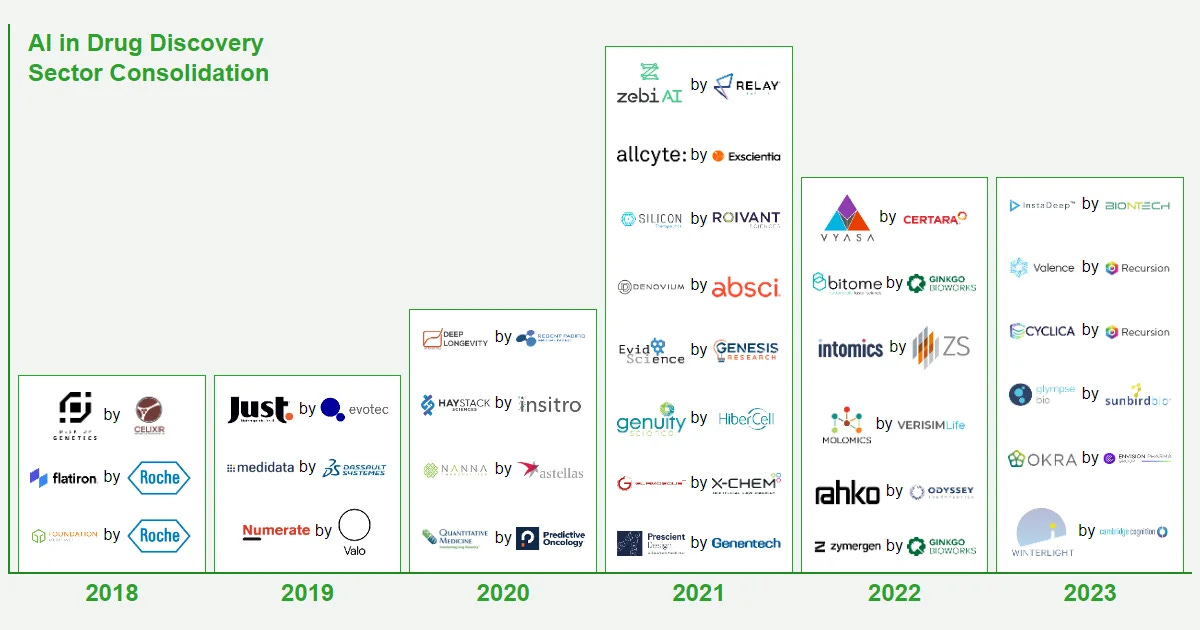
💰 Utah-based 'techbio' company Recursion acquired UK-based AI-drug discovery pioneer Exscientia in arguably the largest AI in bio deal so far.
Recursion Pharmaceuticals (RXRX.O) has agreed to buy smaller rival Exscientia (EXAI.O) for $688 million in an all-stock deal, according to a statement seen by Reuters and further reported by BioPharmaTrend.com.
The deal is reflective of a larger pattern in the AI for drug discovery space, where a consolidation is ongoing with a small number of leading companies taking over smaller or financially troubled players with otherwise strong and innovative technological resources and know-how.
🔬 A busy couple of weeks for AI-driven company Insilico Medicine on two development fronts:
Firstly, Insilico Medicine's AI-designed TEAD inhibitor, ISM6331, received FDA IND approval and Orphan Drug Designation for mesothelioma, with plans to initiate U.S. clinical trials.
Previously, the company announced the launch of DORA, an AI assistant designed to help researchers draft medical papers, and introduced Precious-3 GPT, an open-source AI model for aging research. They also emphasized enhanced data privacy with their offline PandaOmics Box for secure data processing.
📉 Roche is reportedly considering selling its health data subsidiary, Flatiron Health, which it acquired for $1.9 billion in 2018, due to strategic challenges.
Roche's ownership may have unintentionally limited Flatiron's ability to collaborate with other pharmaceutical companies, which has been a key source of its revenue—two-thirds of which comes from selling anonymized cancer patient data to pharma companies.
Despite its continued success of Flatiron in forming partnerships, these collaborations have increasingly involved academic and healthcare organizations rather than pharmaceutical companies, possibly diminishing the strategic value Roche initially sought from the acquisition.
R&D Corner
3D-Printed Blood Vessels Edge Us Closer to Artificial Organs (BiopharmaTrend)
Researchers at Harvard's Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and the John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Science (SEAS) have made a leap in the quest to create artificial organs. Their latest innovation involves 3D printing complex vascular networks that mimic human blood vessels, bringing the reality of implantable human organs closer. The achievement is published in Advanced Materials.
In a reality check for the field, AI underwhelms in Leash Bio's binding contest: 'No one did well' (Endpoints News)
A protein binding contest run by Leash Bio revealed that current AI models struggle with predicting molecules that differ significantly from those they’ve seen before.
In an interview to Endpoints News, Leash Bio's CEO, Ian Quigley, PhD, highlighted that while AI is good at memorizing known data, it performs poorly at extrapolating into novel chemical spaces.
The contest results suggest that random selection of molecules might be as effective as the best models, pointing to limitations in AI’s ability to generalize. These findings raise questions about AI hype, the need for datasets that capture biological complexity, and appropriate benchmarks for AI performance. Leash Bio's strategy to overcome these challenges involves generating far more data, drawing parallels to the successes in chess and protein folding achieved through massive databases.
Quick Hits:
Novel AI Framework for Detecting LLM "Hallucinations" in Medical Summaries
Halda Therapeutics Secures $126 Million in Series B Extension to Advance RIPTAC Cancer Therapies
Lantern Pharma Reports 86% Clinical Benefit in NSCLC Trial, Initial Patient Cohort
Novel AI Framework for Detecting LLM "Hallucinations" in Medical Summaries
23andMe Shifts Focus to Telehealth GLP-1 Prescriptions Amid Strategic Realignment
Persist AI and Nivagen Collaborate on AI-Enhanced Manufacturing for Long-Acting Injectables
Companies to Watch
Six AI-driven Drug Discovery Companies Enabling Precision Oncology
The article discusses how AI is revolutionizing precision oncology through the efforts of six notable companies.
Achilles Therapeutics plc utilizes its PELEUS platform to predict the most potent neoantigens for personalized cancer therapies.
ImmuneAI enhances cell-based immunotherapies with its advanced multiomics technology, exemplified by its work on CAR-NKT cells.
iBio, Inc. combines AI-based antibody optimization with mammalian display technology to develop novel CD3 T-cell binding antibodies.
Evaxion Biotech leverages its AI-Immunology™ platform to develop personalized cancer vaccines, showing success in clinical trials for melanoma.
Lantern Pharma uses its RADR® platform to accelerate the development of oncology drugs, focusing on relapsed non-small cell lung cancer and lymphomas.
Finally, Predictive Oncology employs AI-driven platforms to predict tumor responses to drugs, supported by a vast biobank of human tumor samples, enhancing clinical trial success rates.
Takeaway of the Week
A wonderful and factually-rich report "Biotech financing: darkest before the dawn,” authored by Melanie Senior and published in Nature Biotechnology (2024), provides an in-depth analysis of the current state and future outlook of biotech funding.
You should definitely check out the report, here I am just summarizing briefly some takeaways I found most interesting:
Bifurcated market: There's a stark divide between "haves" and "have-nots" in biotech financing. Companies with clinical-stage assets, experienced management teams, or working in hot therapeutic areas are attracting outsized funding rounds, while early-stage companies struggle.
Larger financing rounds: The average private financing round in 2024 has reached almost $90 million, with at least 50 companies raising rounds worth $100 million or more. Series A rounds are particularly inflated, with an average of $80 million - more than double the average five years ago.
Therapeutic area focus: Obesity, neurology, and immunology are drawing significant investor interest. Companies like Metsera ($290 million seed and series A) and Hercules CM NewCo ($400 million) are capitalizing on the obesity gold rush led by Novo Nordisk's Wegovy and Eli Lilly's Zepbound.
Modality preferences: Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and radioligand therapies (RLTs) are attracting substantial investments. Companies like Tubulis ($139 million) and Pheon Therapeutics ($120 million) have raised significant funds for ADC development. Conversely, cell and gene therapy (CGT) companies are facing challenges, with venture totals, number of financings, and average round sizes all declining steeply.
AI and machine learning impact: AI-driven companies are seeing strong investor interest. Xaira Therapeutics raised a $1 billion Series A round, while EvolutionaryScale secured a $142 million seed round. Overall, AI/ML companies in healthcare research and drug discovery are on track to raise more venture money in 2024 than in any previous year except 2021.
Geographic trends: European biopharma firms are projected to raise more venture funding in 2024 than in any previous year in the last decade and a half, except for 2021. However, Chinese biotech venture funding remains muted in 2024.
Corporate venture capital (CVC) role: CVCs like M Ventures, AbbVie Ventures, and Novo Ventures are playing an increasingly important role in supporting early-stage companies, particularly in Europe.
M&A activity: Significant M&A deals are shaping the landscape, such as AbbVie's $10 billion acquisition of ImmunoGen and Johnson & Johnson's $2 billion purchase of Ambrx, both in the ADC space.
Emerging technologies: Alongside AI, other innovative platforms gaining traction include Orbis Medicines' macrocycle-based technology and companies developing novel approaches in the RLT space.
Public market challenges: While private financing rounds are growing larger, public markets remain muted for biotech companies, with few IPOs in 2024. However, the total raised in the first half of 2024 already surpasses 2022 and 2023 figures.
The biotech financing landscape is showing clear preferences for certain modalities over others. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and radioligand therapies (RLTs) are attracting substantial investments, exemplified by Tubulis's $139 million raise and major acquisitions like Pfizer's $43 billion purchase of Seagen. Conversely, cell and gene therapies (CGT) are facing declining investor interest due to persistent clinical and manufacturing challenges. Meanwhile, AI-driven approaches in protein engineering and drug discovery, along with GLP-1 agonists for metabolic diseases, are seeing a surge in funding, as evidenced by EvolutionaryScale's $142 million seed round and the ongoing obesity gold rush led by Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly.
Bonus Takeaway:
Drug Delivery is Next Big Thing
The success of gene-editing technologies, such as CRISPR, heavily depends on the development of advanced drug delivery systems that can effectively target specific organs in vivo.
According to the insight from a LinkedIn post by Vincent Ling, and original source in STAT article "The race to build better CRISPR delivery vehicles is heating up," current delivery methods, like AAV and LNPs, face significant challenges, including off-target effects and potential toxicity at high doses.
This highlights the crucial, yet often overlooked, role of drug delivery sciences, a field culturally distinct from drug discovery. Innovative companies and labs, including Recode (lung-targeted LNPs), Broad/MIT (AAVs crossing the BBB), and Aera Therapeutics (endogenous virus-like particles), are leading efforts to overcome these barriers.
Despite the massive value created by genetic breakthroughs, there is a growing recognition of the complexities involved in creating a true therapeutic product.
The tide is turning on awareness of these challenges, as seen in the significant investments in delivery technology, such as the $193M raised by Aera Therapeutics.


Great edition! Given the need for vastly larger datasets to improve AI’s predictive power, I wonder if AI will have to work hand in hand with traditional drug discovery techniques to fully realize its potential. the way companies like Absci are combining generative AI with cutting edge cancer research seems to be a promising step in this direction.